

This type of cell division is called binary (prokaryotic) fission. Karyokinesis is unnecessary because there is no true nucleus and thus no need to direct one copy of the multiple chromosomes into each daughter cell. As we’ve seen with bacterial cells, the genome consists of a single, circular DNA chromosome therefore, the process of cell division is simplified. The genomic DNA must be replicated and then allocated into the daughter cells the cytoplasmic contents must also be divided to give both new cells the cellular machinery to sustain life. To achieve the outcome of cloned offspring, certain steps are essential. In unicellular organisms, daughter cells are individuals. In both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, the outcome of cell reproduction is a pair of daughter cells that are genetically identical to the parent cell. For unicellular organisms, cell division is the only method to produce new individuals. Prokaryotes, such as bacteria, produce daughter cells by binary fission. Explain how FtsZ and tubulin proteins are examples of homology.

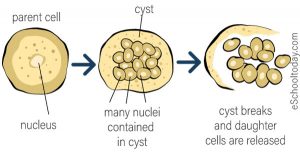
Describe the process of binary fission in prokaryotes.By the end of this section, you will be able to do the following:


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
